THE IMPACT OF THE REPO RATE ON YOUR HOME LOAN
If you hold any kind of debt, it is important to keep a close eye on interest rates: as interest rates go up, so do your monthly repayments. The interest rate that your bank charges is based on the repo rate which is set by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB). To help you stay on top of this, we’ll explain what the repo rate is, how it is set, and, critically, its impact on your home loan.
What’s the difference between the prime lending rate & the repo rate?
The repurchase rate, usually shortened to repo rate, is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money from the SARB. The repo rate is the tool that the Monetary Policy Committee uses to manage inflation, economic growth, and financial stability in the South African economy. The repo rate is a policy mechanism that central banks in other countries (including the United States and the United Kingdom) use to control inflation.
On the other hand, the Prime Lending Rate (often shortened to just Prime) is the rate that commercial, or retail banks will charge their customers. Effectively, Prime is the one you need to worry about, as this is the base fee that the bank works off when deciding what percentage interest rate they will charge you for borrowing money, whether it’s your home loan, vehicle finance, and/or credit card. Depending on your credit score, you will either be charged a rate above or below Prime.
What causes inflation?
Without getting into a full-blown economics lecture, the two key factors that can cause inflation are increased demand for something that’s in short supply, and/or geopolitical events or natural disasters that can result in either shortages and/or higher production prices. When goods are in short supply, and there is high demand for an item, the price for that item goes up. This can often also have a knock-on effect. For example, if fuel prices increase, then delivery costs increase, which means that consumer goods prices increase, etc., etc. To cover the increased costs and still make a profit, everyone in the production chain has to charge more. This is essentially what is referred to when we talk about inflation.
What happens when the repo rate changes?
When the repo rate changes, so does the prime lending rate. If you have a home loan, the bank adjusts your monthly instalment to accommodate that change.
It is also worth keeping in mind that if you have investments and savings, changes in interest rates will also affect what your investments earn: as the interest rate goes up, so your return goes up, and as they drop, so your return will also reduce.
The SARB’s Monetary Policy Committee meets six times a year — in alternate months, starting in January — and it is at these meetings that they make decisions about the interest rate. This means that, in theory, the repo rate could change six times a year. The graph below shows the changes in the repo rate between January 2022 and January 2024, and in that time, the repo rate changed 13 times.
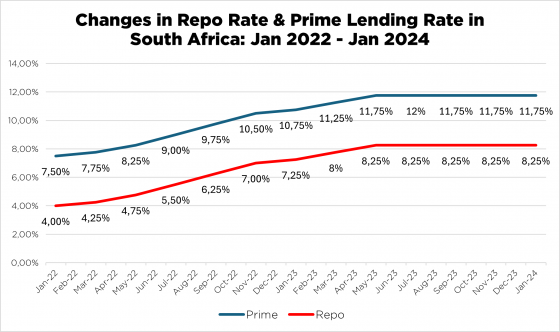
What happens to your bond instalment when the repo rate increases?
When the repo rate increases, your bond instalment will also increase. The only time that it will not go up is if you have a fixed interest rate as part of your home loan agreement.
If you are in the process of buying property and finalising your home loan, the bank may offer you the option of a fixed or variable interest rate. In a rising interest rate cycle, it’s very tempting to choose the fixed rate option. However, there are two things to bear in mind: firstly, the interest rate that the bank will offer you, is often higher than the variable option. Secondly, because it’s very difficult to predict shifts in the interest rate, a variable interest rate allows you to benefit from any possible drops in interest rate, which you can’t if you have fixed your interest rate.
An increase in the interest rate can impact the property market: if there are a series of consecutive rate increases, homeowners must fork out more and more for their home loan instalment each month. When we are in what the experts refer to as a rising interest rate cycle, the property market often gets saturated as stressed homeowners find it more and more difficult to service their bonds and decide to downscale and put their homes on the market. This can also have a negative effect on property prices.
What happens to your bond instalment when repo rate decreases?
It goes without saying that when the repo rate drops, so does the prime lending rate and your bond instalment. At this point, it can be very tempting to opt for a fixed interest rate on your home loan, but again, if the cycle is shifting to one where there could possibly be further reductions in interest rate, you would not benefit.
Word to the wise: if there is a reduction in interest rates, and you can afford it, keep your repayment at the same level because it will help you to pay off your home loan more quickly, saving on interest and other admin costs.
When interest rates start dropping, prospective home buyers begin to feel that owning property becomes more affordable. This means that there are more buyers on the market, but this doesn’t always mean that people are selling, and we see the principle of supply and demand coming into play, and property prices are then likely to increase.
How does the repo rate affect the economy?
The SARB uses the repo rate as a tool to keep inflation in the target range of 3-6%. When the SARB increases interest rates, making it more expensive to borrow money, people tighten their belts, and spend less which helps to curb inflation. Interest rates, globally, have been high and are beginning to drop. Traditionally, though, South Africa’s interest rates tend to be a little higher than international trends which can have the benefit of attracting international investors which, in turn, can bolster economic growth.
Trying to gauge what might happen to interest rates is almost like looking into a crystal ball, and is best left to the experts. However, if you are in two minds about buying a new home and need property advice, contact your nearest RE/MAX office.
Have more unanswered questions? Here are some related questions – and answers – that might help…
How do banks calculate interest rate on loans?
Banks calculate interest on home loans every day, based on the outstanding balance of your loan, and over the period or term of your loan.
What is the current interest rate for home loans in South Africa?
As of January 2024, the prime interest rate is 11.25%. This is the default or base rate for all home loans. However, the interest rate that the bank will charge on your bond will depend on a number of factors including whether you have put down a deposit on the property, your disposable income and, of course, your credit score.
How does the repo rate affect a fixed deposit?
Just as with any financial instrument that either earns or on which interest is charged, the interest you earn on your fixed deposit will track – up or down – with the changes in the repo rate.
